الاتفاق بين لبنان وإسرائيل قد لا يستحق العناء
ديفيد شينكر/ معهد واشنطن/16 أيار/2024
An Israel-Lebanon Agreement May Not Be Worth the Costs
David Schenker/The Washington Institute/May 16/ 2024
The lesson from past deals involving Hezbollah is clear: the group will try to pocket any U.S. concessions on the presidency and other issues while simply jettisoning whatever border commitments it may make in return.
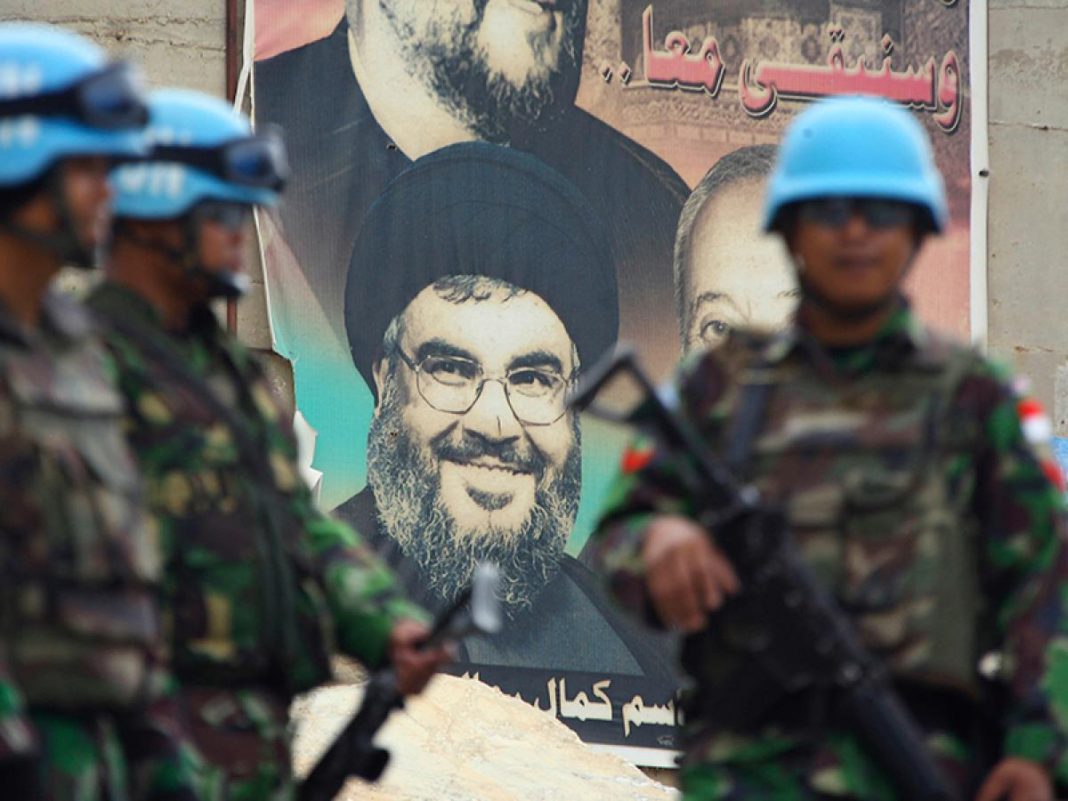
All eyes are on Gaza as Israel and Hamas inch toward a ceasefire in their months-long war. If and when a truce is reached, however, the Biden administration’s focus will likely turn to Lebanon, where it hopes to de-escalate amid fears of a full-scale war. Last week, several local and pan-Arab press outlets reported on Beirut’s unenthusiastic response to a proposal that Washington formulated in partnership with Paris and conveyed to Lebanese and Hezbollah officials via an unofficial French white paper. Although actual negotiations will not begin in earnest until a ceasefire is reached in Gaza, the initial reception from Lebanon suggests that the chances for success are remote.
Outlines of the Proposed Deal
U.S. envoy Amos Hochstein and French minister for Europe and foreign affairs Stephane Sejourne have visited Beirut repeatedly in recent months to lay the groundwork for a joint de-escalation plan, culminating in the white paper. Building on UN Security Council Resolution 1701—which effectively ended the 2006 war between Hezbollah and Israel but failed to secure an enduring peace—the new proposal seeks to fix flaws in the original document that hindered implementation, eroded confidence, and contributed to long-term instability along the border. Key elements of the U.S.-French initiative include:
Redeploying Hezbollah’s Radwan special forces seven to ten kilometers north of the border, close to but not necessarily beyond the Litani River
Stationing 15,000 troops from the Lebanese Armed Forces (LAF) along the frontier
Allowing the UN Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL) and its nearly 11,000 troops to conduct less restricted patrols in south Lebanon unaccompanied by the LAF
Building observation posts near the border to be staffed by the LAF and/or UNIFIL
Ending Israeli military overflights of Lebanon
Establishing a monitoring committee to discuss any infringements of the new arrangement, similar to the body created after Israel’s 1996 military campaign in Lebanon
Initiating negotiations on some disputed border points with an eye toward more formally and precisely defining the UN-demarcated Blue Line
These steps would be complemented by European funding to underwrite LAF operations in the south, as well as U.S. local development assistance and investment promotion.
Negative Response
Arab media reported immediate objections to several aspects of the proposal. The Lebanese paper Nida al-Watan noted that Hezbollah flatly rejected the plan, while the reliably pro-Hezbollah daily al-Akhbar indicated that Speaker of Parliament Nabih Berri had rejected the provisions on repositioning Hezbollah forces, giving UNIFIL freedom of movement in the south, and creating an internationally directed role for the LAF in the south.
The proposal was also vetted by a pair of Hezbollah advisors dubbed the “Khalilan” or “two Khalils”—namely, Hussein Khalil and Ali Hassan Khalil, the latter a Berri confidant who was designated by the U.S. Treasury Department in 2019 for his ties to the militia and assorted corrupt activities. Per Nida al-Watan, they did not explicitly reject or accept the plan, but rather “subjected it to a process of careful hollowing out” that seemingly amounted to the same end result as Berri’s objections. The pan-Arab daily Asharq al-Awsat described the Khalilan’s approach as “buying time” until a Gaza ceasefire is reached and Hochstein returns to Beirut for negotiations.
Sweetening the Deal for Hezbollah?
Although the United States and France appear to be mostly on the same page regarding a potential deal on south Lebanon, they disagree on whether and how the deal should be tied to choosing Lebanon’s next president, a post that has been vacant since October 2022. While the French have refused to connect the two issues, Hochstein has reportedly linked them—though it is unclear how reliable these reports are given that they were published by the pro-Hezbollah al-Akhbar. (Notably, the paper also claimed that Hochstein is not coordinating with Paris on this matter, and that “France is very disturbed by the way the American side has behaved.”)
By law, the presidency must be held by a Maronite Christian, but parliament’s selection of Maronite candidates has been complicated—Hezbollah is pushing for the Syria-aligned leader of the Marada Movement, Sleiman Frangieh, while opponents favor more neutral figures. This decision is relevant to the U.S.-French plan because a president will eventually be required to ratify any border agreement. Given Hezbollah’s rejection of the current terms, the group will likely seek concessions in return for moving its Radwan forces. In theory, delineating the border would seem like a sufficient tradeoff, but Hezbollah may not actually want to resolve the border dispute given that its articulated raison d’etre is fighting the Israeli “occupation” of Lebanon. A more appealing accomplishment for the group would be securing Frangieh’s appointment as president, and Washington seems poised to consider that concession. Perhaps concerned about facilitating another six years of a weak, Iran-friendly Lebanese president, Paris has thus far been uncharacteristically hesitant to adopt such an expedient approach.
Doha Agreement Redux
The Biden administration’s apparent coupling of these issues is reminiscent of the May 2008 Doha agreement, a Qatari-brokered accord reached during a previous Lebanese domestic crisis and presidential vacuum. That crisis emerged after the formerly pro-Western government in Beirut attempted to weaken Hezbollah’s control over the country’s international airport and restrict its secure communications network, spurring the militia to march on the capital and engage in armed clashes that killed nearly a hundred people.
The resultant agreement made crucial concessions to Hezbollah, including a “blocking third” in the cabinet and effective veto power over all government decisions. Ironically, the parties also agreed to prohibit the “use of weapons and violence” to resolve domestic political disputes, giving the state full “security and military authority over Lebanese nationals.” Regarding the vacant presidency, they agreed that parliament would convene and name LAF commander Gen. Michel Suleiman to the post within twenty-four hours of signing the accord. Hezbollah apparently viewed Suleiman as acceptable because the LAF had abstained from intervening during the group’s assault on Beirut. Unsurprisingly, he never once challenged Hezbollah’s writ during his subsequent six years in office.
In short, the Doha agreement was a boon for Hezbollah, consolidating its domestic political dominance at no cost. The group predictably ignored its commitment to renounce violence against its fellow citizens—since 2008, Hezbollah is the leading suspect in at least seven assassinations of prominent opponents in the political and security establishment, among numerous other examples of attacking or intimidating people who get in the way of its local activities. Likewise, Hezbollah—not the “state”—remains the top military and security authority in Lebanon.
Conclusion
Although negotiating a deal for a new status quo on the border might temporarily defer the next war between Israel and Hezbollah, doing so at the cost of installing a president who is obeisant to the militia will not help U.S. interests, let alone the interests of the Lebanese people. Since 2019, the country has been reeling from a financial crisis, but rather than helping its fellow citizens extricate themselves from this predicament, Hezbollah is actively exploiting the crisis while opposing necessary reforms. A pro-Hezbollah president is just as unlikely to pursue such reforms. Moreover, the perception that the Biden administration is considering concessions to Hezbollah while apparently avoiding consultations with the group’s Lebanese critics may give U.S. partners in the Middle East further reason to question Washington’s reliability.
Even more important than the perception problem, however, is the likelihood that Hezbollah will not adhere to any deal Beirut reaches with Washington and Paris. The lesson from 2008 is that the group will pocket whichever provisions benefit its position at home and the interests of its sponsors in Iran while ultimately disregarding the rest. Tragically, this lesson was punctuated in brutal fashion five years after the Doha agreement, when former Lebanese minister Mohamad Chatah wrote an open letter to Iranian president Hassan Rouhani pleading for support on implementing Security Council Resolution 1701, including the provisions on deploying the LAF to the border and ending hostilities with Israel. Just days later, Chatah was assassinated, almost certainly by Hezbollah. Hence, any new deal that perpetuates Hezbollah and Iran’s control over Lebanon is doomed to fail in the long run.
Even a deal’s principal short-term benefit—de-escalating ongoing hostilities between Hezbollah and Israel—could prove to be moot. With Blue Line negotiations on the table, Hezbollah may choose escalation to secure a better deal, as it did during the lead-up to the 2022 maritime agreement. The group might also decide to continue firing on Israel even after a Gaza ceasefire. With nearly 80,000 Israeli citizens still evacuated from the north, the Netanyahu government is under growing pressure to take action that enables their return, potentially including military action. Amid new combat operations in Rafah and reported Hezbollah mobilizations in Lebanon, Israeli defense minister Yoav Gallant recently warned that “it could be a hot summer” in the north. Given the complications and costs of getting to a border agreement, he may be right.
**David Schenker is the Taube Senior Fellow at The Washington Institute and director of its Rubin Program on Arab Politics. Previously, he served as assistant secretary of state for Near Eastern affairs from 2019 to 2021.
https://www.washingtoninstitute.org/policy-analysis/israel-lebanon-agreement-may-not-be-worth-costs
https://www.washingtoninstitute.org/ar/policy-analysis/alatfaq-byn-lbnan-wasrayyl-qd-la-ysthq-alna
الاتفاق بين لبنان وإسرائيل قد لا يستحق العناء
ديفيد شينكر/ معهد واشنطن/16 أيار/2024
الدرس المستخلص من الصفقات السابقة التي شملت “حزب الله” واضح: سيحاول الحزب الاستحصال على أي تنازلات أمريكية بشأن رئاسة الجمهورية وغيرها من القضايا بينما يتخلى ببساطة عن أي التزامات بشأن الحدود قد يتعهد بها في المقابل.
تتجه كل الأنظار نحو غزة بينما تتجه إسرائيل و”حماس” نحو وقف إطلاق النار في حربهما المستمرة منذ أشهر. ولكن إذا تم التوصل إلى هدنة، أو عندما يتم التوصل إليها، سيتحول تركيز إدارة بايدن على الأرجح إلى لبنان، حيث تأمل في وقف التصعيد وسط مخاوف من اندلاع حرب واسعة النطاق. ففي الأسبوع الماضي، أفاد عدد من وسائل الإعلام المحلية والعربية عن استجابة باردة من جانب بيروت على مقترح أعدته واشنطن بشراكة مع باريس ونقلته إلى المسؤولين اللبنانيين ومسؤولين في “حزب الله” عبر ورقة بيضاء فرنسية غير رسمية. وعلى الرغم من أن المفاوضات الفعلية لن تبدأ جدياً إلا بعد التوصل إلى وقف لإطلاق النار في غزة، إلّا أن رد الفعل الأولي للبنان تجاه المقترح يشير إلى أن فرص نجاحه ضئيلة.
الخطوط العريضة للاتفاق المقترح
زار المبعوث الأمريكي آموس هوكستين ووزير أوروبا والشؤون الخارجية الفرنسي ستيفان سيجورني بيروت مراراً وتكراراً في الأشهر الأخيرة لوضع أسس خطة مشتركة لوقف التصعيد، والتي بلغت ذروتها في الكتاب الأبيض. وبناءً على قرار “مجلس الأمن الدولي رقم 1701” – الذي أنهى فعلياً حرب عام 2006 بين “حزب الله” وإسرائيل لكنه فشل في تأمين سلام دائم – يسعى المقترح الجديد إلى إصلاح العيوب التي شابت الوثيقة الأصلية وأعاقت التنفيذ، وأضعفت الثقة، وساهمت في زعزعة الاستقرار على طول الحدود على المدى الطويل. وتشمل العناصر الرئيسية للمبادرة الأمريكية الفرنسية ما يلي:
إعادة انتشار قوة “الرضوان” التابعة لـ”حزب الله” على مسافة سبعة إلى عشرة كيلومترات شمال الحدود، بالقرب من نهر الليطاني ولكن ليس بالضرورة وراءه
نشر 15 ألف جندي من الجيش اللبناني على طول الحدود
السماح لـ “قوة الأمم المتحدة المؤقتة في لبنان” (“اليونيفيل”) وعددها البالغ حوالي 11 ألف جندي بإجراء دوريات أقل تقييداً في جنوب لبنان دون مرافقة من الجيش اللبناني
بناء مراكز مراقبة قرب الحدود يشغلها الجيش اللبناني و/أو قوات “اليونيفيل”
إنهاء التحليق العسكري الإسرائيلي فوق لبنان
إنشاء لجنة مراقبة لمناقشة أي انتهاكات للترتيب الجديد، على غرار الهيئة التي تم إنشاؤها بعد الحملة العسكرية الإسرائيلية في لبنان عام 1996.
البدء بمفاوضات بشأن بعض النقاط الحدودية المتنازع عليها مع التركيز على تحديد “الخط الأزرق” الذي رسمته الأمم المتحدة بشكل أكثر رسمية ودقة
وسيتم استكمال هذه الخطوات من خلال تمويل أوروبي لضمان عمليات الجيش اللبناني في الجنوب، بالإضافة إلى المساعدة الإنمائية المحلية الأمريكية وترويج الاستثمار.
الرد السلبي
أفادت وسائل الإعلام العربية عن اعتراضات فورية على عدة جوانب من المقترح. فقد أشارت صحيفة “نداء الوطن” اللبنانية إلى أن “حزب الله” رفض الخطة رفضاً قاطعاً، في حين أشارت صحيفة “الأخبار” اليومية المعروفة بتأييدها لـ “حزب الله” إلى أن “رئيس مجلس النواب” نبيه بري رفض البنود المتعلقة بإعادة انتشار قوات “حزب الله”، مما يمنح “اليونيفيل” حرية الحركة في الجنوب، وإسناد دور موجه دولياً للجيش اللبناني في الجنوب.
ودرس المقترح أيضاً مستشاران من قبل “حزب الله” ملقبان بـ”الخليلَين”، وهما حسين خليل وعلي حسن خليل، علماً أن هذا الأخير هو من المقربين من بري وقد صنفته وزارة الخزانة الأمريكية (على قائمة الإرهاب) في عام 2019 على خلفية علاقاته بالميليشيا وأنشطة فاسدة متنوعة. ووفقاً لـ “نداء الوطن”، فإنهما لم يرفضا الخطة ولم يقبلاها صراحة، إلا أنهما “أفرغاها من مضمونها” مما أسفر على ما يبدو عن الاعتراضات ذاتها التي أعربها بري. ووصفت صحيفة “الشرق الأوسط” اليومية العربية مقاربة الخليلَين (أي تعاطي الثنائي الشيعي “حزب الله و “حركة أمل”) بأنه “شراء الوقت” إلى أن يتم التوصل إلى وقف لإطلاق النار في غزة وعودة هوكستين إلى بيروت لإجراء مفاوضات.
تحلية الصفقة لـ “حزب الله”؟
على الرغم من أن الولايات المتحدة وفرنسا تبدوان في الغالب على الموجة ذاتها فيما يتعلق باتفاق محتمل بشأن جنوب لبنان، إلا أنهما تختلفان حول ما إذا كان ينبغي ربط الاتفاق باختيار رئيس الجمهورية المقبل في لبنان وكيفية القيام بذلك، وهو المنصب الذي ظل شاغراً منذ تشرين الأول/أكتوبر 2022. وبينما رفض الفرنسيون الربط بين القضيتين، إلّا أن هوكستين ربطهما ببعضهما البعض وفقاً لبعض التقارير – على الرغم من أنه من غير الواضح مدى موثوقية هذه التقارير بالنظر إلى أنها نُشرت من قبل صحيفة “الأخبار” الموالية لـ “حزب الله”. (والجدير بالذكر أن الصحيفة زعمت أيضاً أن هوكستاين لا ينسق مع باريس بشأن هذه المسألة، وأن “فرنسا منزعجة للغاية من الطريقة التي يتصرف بها الجانب الأمريكي”.)
وبموجب القانون، يجب أن يتولى منصب الرئاسة مسيحي ماروني، لكن اختيار البرلمان للمرشحين الموارنة معقد، إذ أن “حزب الله” يضغط باتجاه زعيم تيار “المردة” سليمان فرنجية، الذي يُعد حليف النظام السوري، في حين يفضل المعارضون شخصيات أكثر حيادية. ويُعتبر هذا القرار ذو صلة بالخطة الأمريكية الفرنسية، لأنه سيتعين على الرئيس في النهاية التصديق على أي اتفاق حدودي. ونظراً لرفض “حزب الله” للشروط الحالية، سيسعى الحزب على الأرجح للحصول على تنازلات مقابل نقل قوة “الرضوان” التابعة له. ونظرياً، قد يبدو ترسيم الحدود مقايضة كافية، لكن “حزب الله” قد لا يرغب فعلياً في حل النزاع الحدودي لأن السبب الواضح لوجوده هو محاربة “الاحتلال” الإسرائيلي للبنان. ويلاقي إنجاز آخر استحساناً أكبر لدى الحزب وهو تعيين فرنجية رئيساً، ويبدو أن واشنطن مستعدة للنظر في إمكانية القيام بهذا التنازل. وربما تكون باريس، التي تشعر بالقلق إزاء تسهيل حكم رئيس لبناني ضعيف صديق لإيران على مدى ست سنوات أخرى، مترددة حتى الآن على نحو غير معهود في تبني مثل هذا النهج النفعي.
إعادة إحياء اتفاقية الدوحة
يذكّر ربط إدارة بايدن على ما يبدو لهاتين القضيتين باتفاق الدوحة من أيار/مايو 2008، وهو اتفاق تم التوصل إليه بوساطة قطرية خلال أزمة داخلية لبنانية سابقة وفراغ رئاسي. فقد ظهرت هذه الأزمة بعد أن حاولت الحكومة الموالية للغرب سابقاً في بيروت إضعاف سيطرة “حزب الله” على المطار الدولي في البلاد وتقييد شبكة اتصالاته الآمنة، مما دفع الميليشيا إلى الزحف إلى العاصمة والانخراط في اشتباكات مسلحة أسفرت عن مقتل ما يقرب من مائة شخص.
وقد قدم الاتفاق الناتج عن ذلك تنازلات حاسمة لـ”حزب الله”، بما في ذلك “الثلث المعطل” في مجلس الوزراء وحق نقض فعلي على جميع قرارات الحكومة. ومن المفارقات أن الأطراف اتفقت أيضاً على حظر “استخدام الأسلحة والعنف” لحل النزاعات السياسية الداخلية، مما منح الدولة “السلطة الأمنية والعسكرية الكاملة على المواطنين اللبنانيين”. وفيما يتعلق برئاسة الجمهورية الشاغرة، اتفقت الأطراف على أن يجتمع مجلس النواب ويعيّن قائد الجيش العماد ميشال سليمان لهذا المنصب خلال أربع وعشرين ساعة من توقيع الاتفاق. ويبدو أن “حزب الله” اعتبر سليمان مقبولاً لأن الجيش اللبناني امتنع عن التدخل أثناء هجوم الحزب على بيروت. ومن غير المستغرب أن سليمان لم يتحدى مطلقاً أوامر “حزب الله” خلال السنوات الست اللاحقة التي قضاها في منصبه.
باختصار، كان اتفاق الدوحة بمثابة نعمة لـ”حزب الله”، حيث عزز هيمنته السياسية الداخلية دون أي تكلفة. وقد تجاهل الحزب، كما كان متوقعاً، التزامه بنبذ العنف ضد أبناء وطنه. فمنذ عام 2008، أصبح “حزب الله” المشتبه به الرئيسي في سبع عمليات اغتيال على الأقل لمعارضين بارزين ضمن المؤسسة السياسية والأمنية، من بين العديد من الأمثلة الأخرى لمهاجمة أو ترهيب كل من يعترض أنشطته المحلية. وبالمثل، يظل “«حزب الله” – وليس “الدولة” – هو السلطة العسكرية والأمنية العليا في لبنان.
الخاتمة
على الرغم من أن التفاوض على صفقة لإرساء وضع راهن جديد على الحدود قد يؤدي مؤقتاً إلى تأجيل الحرب المقبلة بين إسرائيل و”حزب الله”، إلا أن القيام بذلك على حساب تنصيب رئيس جمهورية خاضع للميليشيا لن يخدم المصالح الأمريكية، ناهيك عن مصالح الشعب اللبناني. فمنذ عام 2019، ترزح البلاد تحت وطأة أزمة مالية، ولكن بدلاً من أن يساعد “حزب الله” أبناء وطنه على الخروج من هذا المأزق، يستغل الأزمة بشكل نشط بينما يعارض الإصلاحات الضرورية. ومن غير المرجح أن يتابع رئيس مؤيد لـ “حزب الله” مثل هذه الإصلاحات. علاوة على ذلك، فإن التصوّر بأن إدارة بايدن تدرس تقديم تنازلات لـ “حزب الله” بينما تتجنب على ما يبدو المشاورات مع المنتقدين اللبنانيين للحزب قد يعطي شركاء الولايات المتحدة في الشرق الأوسط سبباً إضافياً للتشكيك في موثوقية واشنطن.
لكن الأهم من مشكلة التصوّر هو احتمال عدم التزام “حزب الله” بأي اتفاق تتوصل إليه بيروت مع واشنطن وباريس. فالعبرة المستقاة من عام 2008 هي أن الحزب سيحصل على أي بنود تخدم مكانته في الداخل ومصالح رعاته في إيران بينما يتجاهل في النهاية الأحكام المتبقية. وللأسف، تجسّدت هذه العبرة بطريقة وحشية بعد خمس سنوات من اتفاق الدوحة، عندما كتب الوزير اللبناني السابق محمد شطح رسالة مفتوحة إلى الرئيس الإيراني حسن روحاني يناشده فيها دعم تنفيذ “قرار مجلس الأمن رقم 1701″، بما في ذلك الأحكام المتعلقة بنشر الجيش اللبناني على الحدود وإنهاء الأعمال العدائية مع إسرائيل. وبعد أيام فقط، اغتيل شطح، على يد “حزب الله” بشكل شبه مؤكد. ومن ثم، فإن أي اتفاق جديد يديم سيطرة “حزب الله” وإيران على لبنان محكوم عليه بالفشل على المدى الطويل.
وحتى الفائدة الرئيسية للصفقة على المدى القصير، المتمثلة بوقف تصعيد الأعمال العدائية المستمرة بين “حزب الله” وإسرائيل، قد تكون موضع نقاش. فمع طرح مفاوضات “الخط الأزرق” على الطاولة، قد يختار الحزب التصعيد لضمان التوصل إلى اتفاق أفضل، كما فعل خلال الفترة التي سبقت الاتفاق البحري لعام 2022. وقد يقرر الحزب أيضاً مواصلة إطلاق النار على إسرائيل حتى بعد وقف إطلاق النار في غزة. فمع استمرار إجلاء ما يقرب من 80 ألف مواطن إسرائيلي من شمال البلاد، تتعرض حكومة نتنياهو لضغوط متزايدة لاتخاذ إجراءات من شأنها تمكين عودتهم، وربما يشمل ذلك العمل العسكري. وفي خضم العمليات القتالية الجديدة في رفح والتقارير عن عمليات التجنيد التي يجريها “حزب الله” في لبنان، حذر وزير الدفاع الإسرائيلي يوآف غالانت مؤخراً من أن “الصيف قد يكون حاراً” في الشمال. ونظراً للتعقيدات والتكاليف المرتبطة بالتوصل إلى اتفاق حدودي، فقد يكون على حق.
**ديفيد شينكر هو “زميل أقدم في برنامج توب” في معهد واشنطن، ومدير “برنامج «روبين فاميلي» حول السياسة العربية” التابع للمعهد. وشغل سابقاً منصب مساعد وزير الخارجية الأمريكي لشؤون الشرق الأدنى من عام 2019 إلى عام 2021.