The Pope and Holy War
Denis MacEoin/Gatestone Institute/August 03/16
The West that jihadists now terrorize has allowed itself to be weakened. A combination of political correctness, fear of giving offense, fear of combat, and a reluctance to upset illusory stability has led to an incredible series of opportunities for the jihadists.
We have dropped our guard and turned away. Not because we have no security forces. We do. But because we often are not looking at the right things: the texts and sermons that prefigure radicalisation.
“[T]he Noble Quran appoints the Muslims as guardians over humanity in its minority, and grants them the rights of suzerainty and dominion over the world in order to carry out this sublime commission. … We have come to the conclusion that it is our duty to establish sovereignty over the world and to guide all of humanity to the sound precepts of Islam and to its teachings…” — Hassan al-Banna, founder of the Muslim Brotherhood.
On the morning of July 26, a priest serving mass, an elderly man of 85, Father Jacques Hamel, was butchered before his altar by one of two knife-wielding devotees of the Islamic State. His killer slit his throat and might very well have proceeded to behead him, as is the wont of many jihadi executioners. The followers of a faith that honours murderers as martyrs (shuhada’) created a martyr for quite another faith.
In both Greek and Arabic, the terms “martyr” and shahid mean exactly the same thing: “a witness”. Father Hamel was the latest in a long line of Christian martyrs who have been slain by men of violence, supposedly in order to attest to the sole truth of their faith. Many Muslim martyrs have died in much that way, but even more have given their lives while waging war (jihad) to conquer territories for Islam.[1]
The flag of the Islamic State reads “la ilaha illa’llah, Muhammadun rasulu’llah”. The words mean: “There is no God but God; Muhammad is the prophet of God”. Those two phrases are known as the shahada, the bearing of witness. You see it everywhere today, now in Syria, then again in France or the UK. But shahada also means martyrdom. And martyrdom while committing violence is what the killers of an innocent man of God achieved on that day when armed police found them and shot them dead outside the church they had desecrated.
On the following day, the head of the Catholic Church, Pope Francis, issued a statement on the event, and for a moment it seemed that he had finally got things right. He said the world was now at war. Decades after the war started, here was a religious leader and statesman who seemed to have awakened to the fact that Western countries have been unwillingly and ineffectively failing to wage a war against Islamic radicalism. Or perhaps it is more accurate to say that Islamic radicalism has been waging a war with us.
But then he blew it. What he then said was:
“It’s war, we don’t have to be afraid to say this … a war of interests, for money, resources. I am not speaking of a war of religions. Religions don’t want war. The others want war.”
What? Is slaughtering a priest at his altar linked to “interests, money, resources”? Were the killers driven by a longing for social justice, for more money, for access to greater resources? Did they think the violent death of a harmless priest would bring them any of that? They had not gone to steal any of the valuable altar table objects, the censers, the candlesticks, the crucifix, the monstrance. The killers had been shouting “Allahu akbar”, literally “God is greater” (than everything, especially, to Muslims, the supposedly non-monotheistic Christian Trinity and the Church). As we know only too well, “Allahu akbar” is a religious phrase that Muslims use often. It is the beginning of the call to prayer, the adhan, repeated six times, five times a day, preceded and followed by the shahada. It has been ringing in Western ears every time Muslims in Europe and North America carry out attacks or as a prelude to a suicide attack. It is precisely because Muslims believe that their God (named in Arabic as Allah) is superior to all other gods, because to them Islam is the greatest of all religions and lastly, because Islam is destined to conquer the world either by conversion or through violence.
What did Pope Francis mean when he said “Religions don’t want war. The others want war”? This is a man with access to endless colleges of scholars, to academics worldwide, to specialists in Islam and the Middle East. It is simply not true. To begin with, who are these “others”? Non-religious people? Atheists? Agnostics? Protestants?
In order to win a war, you have to be able to identify your enemy, understand his motives, figure out just what drives his soldiers to risk their lives in battle, know for what cause mothers and wives should send their sons and husbands to fight, knowing they may never return. Ignore all that, invent false motives for the enemy, or fail to know his ultimate aims, and you will lose. “If you know the enemy and know yourself you need not fear the results of a hundred battles”, said the great Chinese general, Sun Tzu, in his Art of War.
A day after that remark, the Pope sadly compounded his ignorance. A report in a Catholic magazine, Crux, stated that:
The pope said that in every religion there are violent people, “a small group of fundamentalists,” including in Catholicism.
“When fundamentalism goes as far as murdering … you can murder with your tongue and also with the knife,” he said.
“I believe that it’s not fair to identify Islam with violence. It’s not fair and it’s not true,” he continued, adding that he has had a long conversation with the Grand Imam of Al-Azhar, the Cairo-based Islamic university often described as the Vatican of the Sunni world.
“I know how they think. They look for peace, encounter,” he said. [Author’s italics]
Unfortunately, it is clear that the Pope (along with hundreds of politicians and religious leaders in the West, although not in Israel) does not know his enemy at all. If he thinks that “religions do not want war,” it is also clear he has never studied Islam or received truthful instruction in it from anyone. Here is why.
The later chapters of the Qur’an contain dozens of verses calling on the believers to go out to fight jihad or to use their resources to pay others to do so. The purpose of jihad is “the strengthening of Islam, the protection of believers and voiding the earth of unbelief”.[2]
According to a modern expert on jihad, “the Qur’an… presents a well-developed religious justification for waging war against Islam’s enemies”.[3]
Islam is not merely a religion; it is a system of governance. Here is Hassan al-Banna, the founder of the ubiquitous Muslim Brotherhood:
Islam is a comprehensive system which deals with all spheres of life. It is a state and a homeland (or a government and a nation). It is morality and power (or mercy and justice); it is a culture and a law (or knowledge and jurisprudence). It is material and wealth (or gain and prosperity). It is an endeavour and a call (or an army and a cause). And finally, it is true belief and worship.[4]
What does this mean for non-Muslims? Banna again makes this clear:
This means that the Noble Quran appoints the Muslims as guardians over humanity in its minority, and grants them the rights of suzerainty and dominion over the world in order to carry out this sublime commission. Hence it is our concern, not that of the West, and it pertains to Islamic civilization, not to materialistic civilization. We have come to the conclusion that it is our duty to establish sovereignty over the world and to guide all of humanity to the sound precepts of Islam and to its teachings, without which mankind cannot attain happiness.[5]
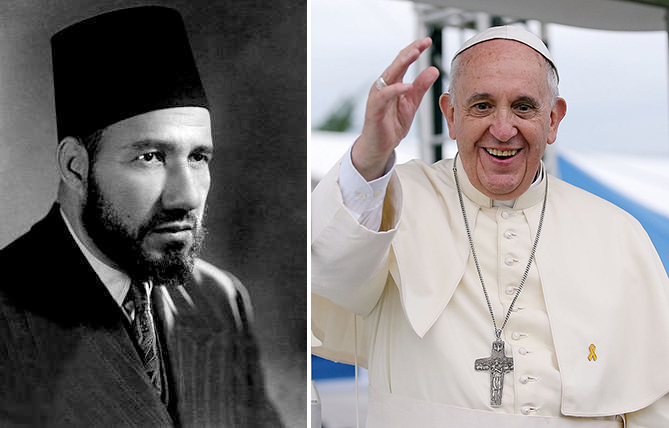
Pope Francis (right), recently said that “I am not speaking of a war of religions. Religions don’t want war,” and “I believe that it’s not fair to identify Islam with violence. It’s not fair and it’s not true.” Hassan al-Banna (left), founder of the Muslim Brotherhood, wrote that “the Noble Quran appoints the Muslims as guardians over humanity in its minority, and grants them the rights of suzerainty and dominion over the world in order to carry out this sublime commission.”
The Islamic Tradition literature, found in the six canonical collections, lays down descriptions of jihad and instructions on how to fight it. Please do not be misled by the oft-repeated obfuscation, “The greater jihad is a struggle with the self, a spiritual war”. There is no mention of this idea in the classical texts.[6] For centuries, jihad has meant physical warfare. Even the mystical Sufi brotherhoods have engaged in that extremely physical struggle.[7]
The Islamic prophet Muhammad led his men into battle on many occasions and sent out around 100 raiding parties and expeditions.[8] His successors, the caliphs, did the same. In the half-century after Muhammad’s death in 632 C.E., Muslim forces had conquered half the known world. Jihad wars continued to be fought on an annual basis by all the great Islamic empires, with no exception.
The first two major Islamic empires, that of the Umayyads (661-750) and their successors under a new dynasty of caliphs, the Abbasids (750-1258) carried out annual expeditions (usually two or more per year) against the Byzantine Empire (based in Constantinople). These raids were an ongoing tradition based on the earliest jihad wars in both the West and the East. They were never haphazard, but well planned. There were usually to two summer campaigns, often be followed by winter expeditions.
The summer jihads usually took the form of two separate attacks. One onslaught was called the “expedition of the left”. It was launched from the border fortresses of Sicily, whose troops were mainly of Syrian origin. The larger “expedition of the right” would be carried out from launched from the eastern Anatolian province of Malatya, deploying Iraqi troops. These jihad expeditions reached their height under the third major empire, that of the Ottomans, who conquered Constantinople in 1453, thereby bringing an end to the Byzantine Empire. Constantinople was renamed Istanbul and its chief basilica, Hagia Sophia, was turned into the imperial mosque of the Ottomans.
Today’s jihadist organizations, from the Islamic State to al-Qaeda, the Taliban, Islamic Jihad, Jabhat al-Nusra, Boko Haram, Hamas, al-Shabaab and hundreds of others are simply carrying out, on a broader canvas, the jihad wars of the nineteenth century.[9]
Jihadists seem to do this in preference to missionary work (although other groups such as the Pakistani Tablighi Jamaat do plenty of that) because their wars hark back to the days of Muhammad and his companions, the first three warlike generations. The term salafi, used now for the most radical Islamic groups, comes from salaf, or “ancestor,” but with a specialized meaning of the first three generations of Islam. Muhammad, his first followers, their children and grandchildren. Jihadists do it because, having lost military strength since the collapse of the Ottoman empire in 1918, they seem still to feel compelled to fight back against the power of the West, the triumph of the Christians (or in Israel, the Jews). God, in their eyes, promised his followers, the Muslims, that they would one day rule the world,[10] and for many centuries, Muslims may have thought that was actually happening. Then such hopes were dashed. Western empires started conquering, colonizing and ruling Muslim states, such as northern India, Algeria, Egypt, Sudan, Libya, and elsewhere — a reversal quite unthinkable.
To fight back, jihadists have chosen to use the best weapon at their disposal: terrorism. Worse, the West they now terrorize has allowed itself to be weakened. A combination of political correctness, fear of giving offense, fear of combat, and a reluctance to upset illusory stability has led to an incredible series of opportunities for the jihadists.
The young Islamist who killed the priest in France, for example, had been twice arrested for trying to head to Syria to serve with the Islamic State. At the time of the murder, the kindly authorities had forced him to wear an ankle bracelet with which to be monitored — but his curfew was only overnight. During the day, he was allowed to wander the streets freely. On that fateful morning, he decided to walk with his companion into a nearby church and fulfil his longings for martyrdom and for killing a Christian.
Unfortunately, Pope Francis could not be more wrong. One religion has wanted to fight wars from its inception. We have had more than 1400 years to guard ourselves against that, as when the Ottoman Empire was stopped at the Gates of Vienna in 1683. Now, we have dropped our guard and turned away. Not because we have no security forces. We do. But because we often are not looking for the right things: the texts and sermons that prefigure radicalisation.
Why do young Muslims turn from ordinariness to recruitment for the extremists? Young Christians, Hindus, Jews, Buddhists, and Baha’is do not move in that direction. Could it be because so many young Muslims, first in the Islamic countries, now in the West, are taught from an early age that Islam aspires to domination, that jihad is not an evil but rather an expression of their faith, that they suffer as victims of “Islamophobia,” that Western women are immoral, and that other religions are false?
It is time to wake up. We are indeed at war, whether we like it or not. “You may not be interested in war, but war is interested in you”, Leon Trotsky said.
Our enemy is an extremist version of Islam that has yet to undergo a reformation, one that takes Muslims not back to the seventh century, but forwards to the twenty-first and possibly beyond.
**Dr. Denis MacEoin, based in England, is an expert on Islam.
[1] “The concept of martyrdom developed differently in Islam than it did in either Judaism or Christianity. Martyrdom in Islam has a much more active sense: the prospective martyr is called to seek out situations in which martyrdom might be achieved.” David Cook, Understanding Jihad, University of California Press, 2015, p. 26.
[2] Rudolph Peters, Islam and Colonialism: The Doctrine of Jihad in Modern History, The Hague, 1979, p. 10
[3] Cook, p. 11.
[4] Hasan al-Banna, Message for Youth, trans. Muhammad H. Najm, London, 1993, p. 6
[5] Wendell Charles (trans), The Five Tracts of Hasan Al-Banna (1906-1949), University of California Press, 1978, pp. 70-73.
[6] “Traditions indicating that jihad meant spiritual warfare… are entirely absent from any of the official, canonical collections (with the exception of al-Tirmidhi, who cites ‘the fighter is one who fights his passions’; they appear most often in the collections of ascetric material or proverbs.” Cook, p. 35.
[7] “This paradigm persisted into medieval times, where we often find the Sufi groups fighting the enemies of Islam. For example, after defeating the Crusaders under Guy de Lusignan at the Battle of the Horns of Hattin (1187), the Muslim leaders Salah al-Din al-Ayyubi [Saladin] (1169-91) gave the captive Crusaders to several of his Sufi regiments to slaughter.” Cook, p. 45.
[8] A comprehensive and fully annotated list is available at Wikipedia.
[9] For details of these, see Rudolph Peters, passim.
[10] “He (God) it is who sent his Messenger [Muhammad] bringing guidance and the True Religion in order to make [Islam] dominant over all other religions” (Qur’an 9:33). The fifth verse of that same sura is known as the “Sword Verse”, because it is the first to encourage physical attacks on non-Muslims.
© 2016 Gatestone Institute. All rights reserved. The articles printed here do not necessarily reflect the views of the Editors or of Gatestone Institute. No part of the Gatestone website or any of its contents may be reproduced, copied or modified, without the prior written consent of Gatestone Institute. https://www.gatestoneinstitute.org/8604/pope-holy-war-jihad